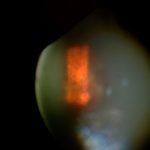
Retina Tear
Retinal tears are a serious eye condition that can potentially lead to retinal detachment if left untreated. Fortunately, modern medicine offers effective treatments for retinal tears, one of which is laser treatment.
What is a Retinal Tear
Retina is the delicate tissue lining the back of the eye that captures light and sends visual signals to the brain. A retinal tear occurs when this tissue tears or separates from the underlying layers. This can lead to a range of visual problems and, if not addressed promptly, may progress to retinal detachment.
Indications for Laser Treatment
Laser treatment is a common approach to manage retinal tears. It’s crucial to identify the situations where this treatment is warranted. Laser treatment for retinal tears is typically recommended in the following scenarios:
- Presence of Symptomatic Retinal Tears: When a patient experiences symptoms like floaters, flashes of light, or sudden vision changes, it may indicate the presence of a retinal tear. In such cases, laser treatment is often considered.
- High-Risk Patients: Patients with a history of retinal tears in one eye are at an increased risk of developing tears in the other eye. Laser treatment may be recommended as a preventive measure in such cases.

Risks of Retinal Detachment
Understanding the risks associated with untreated retinal tears is crucial to emphasize the importance of timely intervention. If a retinal tear progresses to retinal detachment, it can lead to severe vision loss. Some risks associated with retinal detachment include:
- Vision Loss: The detachment of the retina can result in permanent vision loss, especially if it involves the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision.
- Surgical Intervention: Retinal detachment often requires more invasive surgery than treating a retinal tear, increasing the complexity of the procedure and potential complications.
Laser Treatment Procedure
Laser treatment for retinal tears is a relatively straightforward outpatient procedure. It is typically performed in the doctor’s office or an outpatient surgery center. Here’s an overview of the process:
- Pupil Dilation: Before the procedure, your eye surgeon may dilate your pupil using eye drops to ensure a clear view of the retina.
- Numbing the Eye: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the eye, ensuring the patient’s comfort during the procedure.
- Laser Application: Using a special laser, the surgeon directs a precise beam of light onto the retinal tear. The laser creates tiny burns around the tear, essentially “welding” it back in place.
- Post-Procedure Observation: After the procedure, the patient may need to remain at the clinic for a short period of observation to ensure there are no immediate complications.
Common Side Effects
While laser treatment for retinal tears is generally safe and effective, patients may experience some common side effects, including:
- Blurred Vision: Temporary blurred vision is normal after the procedure, but it typically improves within a few hours.
- Floaters: Some patients may notice an increase in floaters immediately after laser treatment, but these usually resolve over time.
- Light Sensitivity: Sensitivity to light may occur temporarily, but it usually diminishes within a day or two.
Post-Operative Outcomes
The goal of laser treatment for retinal tears is to prevent further progression of the tear and the development of retinal detachment. The majority of patients experience positive post-operative outcomes, including:
- Retinal Tear Closure: In most cases, the laser effectively seals the tear, preventing fluid from entering and reducing the risk of detachment.
- Minimal Recovery: Laser treatment typically involves minimal downtime, and patients can usually resume their normal activities within 24 hours.
- Follow ups: Multiple follow ups may be required to monitor success of laser treatment. Occasionally patients may require more than one sitting for the laser treatment.