Epi-Retinal Membrane (ERM)
What is Epi-Retinal Membrane?
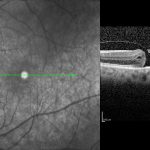
Epi-Retinal Membrane (ERM) is a scar tissue that grows on the macula (the central portion of the retina). Macula is responsible for central sharp vision, that helps in reading and recognizing faces.
What are the symptoms?
An epiretinal membrane will not cause complete blindness. It will generally affect the central vision and cause blurring or distortion (straight lines may seem crooked). The side vision, however, remains unaffected.
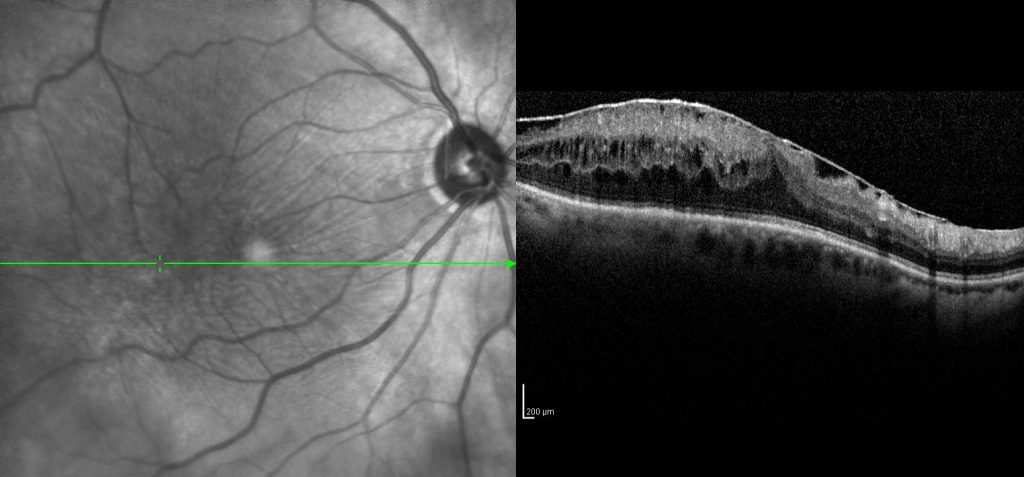
OCT scan showing Epi-Retinal Membrane that is causing retinal swelling (edema).
What causes Epi-Retinal Membrane?
There is no fundamental cause for epiretinal membrane . However, the risk factors include:
- Age over the age of 50
- Diabetes
- History of retinal break/detachment
- Laser or cryo treatment
- Injury to the eye
- Uveitis (inflammation in the eye)
How can it be diagnosed?
Your doctor will perform a dilated retinal exam and may be able to see the membrane. He may advise OCT (optical coherence tomography) test to confirm the diagnosis (see picture above).
How can it be treated?
Not all epiretinal membranes require treatment. If the blurred vision is not dramatically noticeable, the treatment will be unnecessary.
In more severe cases surgery (Vitrectomy) is done to peel the membrane. It is mostly done in local anesthesia, which takes about 40 minutes in the operation theatre. Vision starts improving in 2-3 weeks, but full recovery may take unto 6 months.
Anti-VEGF injections do not improve ERMs.
Courtesy: Dr Paul Sullivan
What are the complications of vitrectomy surgery?
Most patients have a very good outcome. Rare complications include, retinal detachment, regrowth of the membrane, and bleeding inside the eye. Infection is much rarer after vitrectomy surgery.